Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
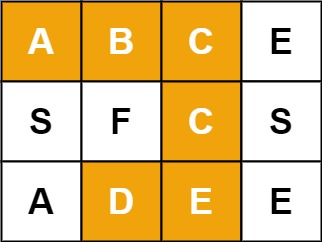
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" Output: true
Example 2:
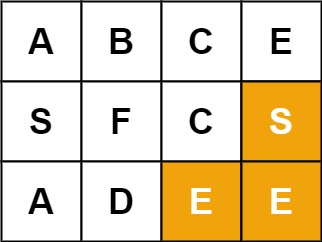
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" Output: true
Example 3:
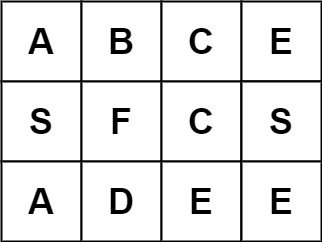
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" Output: false
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15boardandwordconsists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Follow up: Could you use search pruning to make your solution faster with a larger board?
This is my first daily problem and not hard to figure it out that it can be solved by DFS.
class Solution:
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
directions = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
m = len(board)
n = len(board[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
if self.find_word(board, word, i, j, 1):
return True
return False
def find_word(self, board, word, i, j, same_len):
if len(word) == same_len:
return True
directions = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
m = len(board)
n = len(board[0])
current = board[i][j]
board[i][j] = None
for direction in directions:
new_i = i + direction[0]
new_j = j + direction[1]
if 0 <= new_i < m and 0 <= new_j < n and board[new_i][new_j] is not None:
if board[new_i][new_j] == word[same_len]:
result = self.find_word(board, word, new_i, new_j, same_len + 1)
if result:
return True
board[i][j] = current
return False
搶先發佈留言